What Are The Key Factors To Consider When Selecting Between A Continuous Or Indexing Rotating Conveyor?
— Choosing the right conveyor system can make or break your production efficiency when designing or upgrading a manufacturing line.
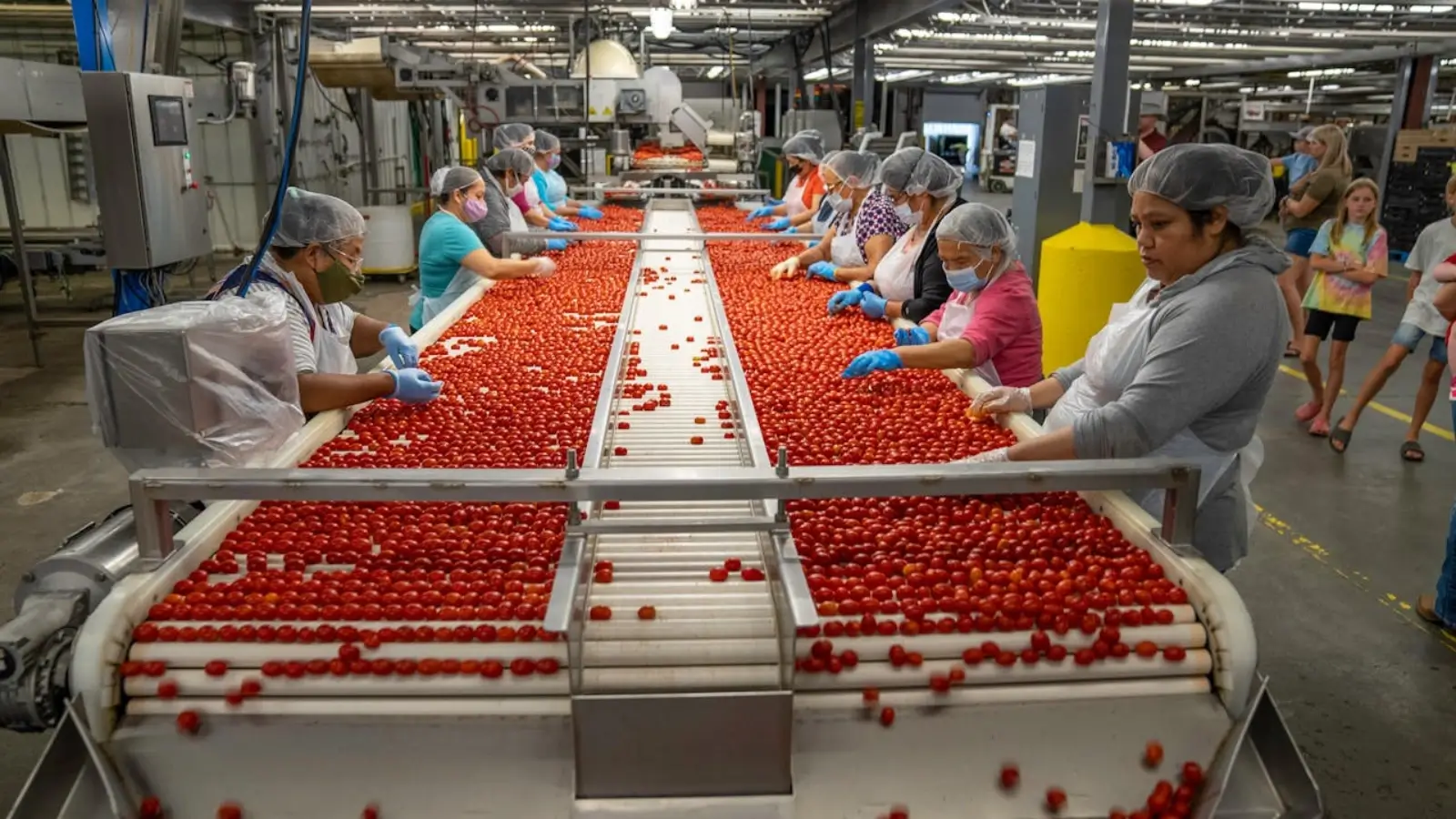

Choosing the right conveyor system can make or break your production efficiency when designing or upgrading a manufacturing line. Making the wrong choice could lead to costly downtime, reduced throughput, and unnecessary maintenance expenses. So, what are the key factors to consider when selecting a continuous or indexing rotating conveyor?
The primary factors are production speed requirements, precision needs, and load handling characteristics. Continuous conveyors are ideal for high-speed, constant-flow operations, while indexing systems better suit applications requiring precise positioning and dwell time at workstations.
While this basic overview provides a starting point, the selection process is much more nuanced. Several other critical factors to evaluate, including maintenance requirements, energy consumption, and compatibility with existing systems, could significantly impact your operation's success. Let's explore these factors in detail to ensure you make the most informed decision for your specific application.
How Does Production Speed Impact Your Choice Between Continuous And Indexing Conveyors?
Production speed requirements play a crucial role in conveyor selection. Continuous rotating conveyors excel in high-speed applications where constant material flow is essential, typically handling rates of 100+ pieces per minute. They're particularly effective in packaging, food processing, and pharmaceutical industries where maintaining consistent throughput is critical.
Indexing conveyors, on the other hand, are better suited for operations requiring periodic stops. They usually handle 20-60 pieces per minute, making them ideal for assembly operations, quality inspection stations, or any process requiring precise positioning and dwell time at specific points.
What Role Does Maintenance And Reliability Play In The Decision?
Maintenance considerations can significantly influence your choice between continuous and indexing systems. Continuous conveyors generally have fewer moving parts and mechanical components, resulting in lower maintenance requirements and reduced downtime. However, when issues do occur, the entire line typically needs to stop for repairs.
Indexing conveyors have more complex mechanical components, particularly in the drive and control systems. While this means more regular maintenance is required, these systems often allow for easier troubleshooting and component replacement. Additionally, some indexing systems can be designed with redundancy, allowing operation to continue even if one station fails.
How Do Space And Layout Requirements Differ Between The Two Types?
Space utilization and layout flexibility vary significantly between continuous and indexing conveyors. Continuous systems typically require more straightforward layouts with gradual curves and longer acceleration/deceleration zones. This can result in a larger footprint, but they generally offer better space efficiency for high-volume operations.
Indexing conveyors often require less overall space but need more clearance around workstations for maintenance access and operator interaction. They're also more adaptable to complex layouts and can more easily accommodate changes in production requirements. However, their start-stop nature means they need robust support structures and may require more vertical space for mechanical components.
What About Energy Consumption And Operating Costs?
Energy efficiency varies significantly between these conveyor types. Continuous rotating conveyors typically consume more energy during operation because they're constantly running, even during lower production periods. However, they avoid the energy spikes associated with frequent starts and stops, which can lead to more predictable power consumption patterns.
Indexing conveyors may have lower overall energy consumption due to their intermittent operation, but they experience higher peak loads during acceleration and deceleration phases. The energy cost difference can be substantial over time, with some facilities reporting 15-25% higher energy costs for continuous systems in comparable applications.
Additionally, the choice between these systems can affect auxiliary costs like cooling and lubrication requirements. Continuous systems often need more consistent lubrication and may require additional cooling systems to prevent overheating during extended operation.
How Does Product Handling Sensitivity Affect Your Conveyor Choice?
Product fragility and handling requirements can be a decisive factor in the selection process. With their smooth, constant motion, continuous rotating conveyors typically offer gentler handling for delicate items. The gradual acceleration and consistent movement reduce the risk of product damage, making them ideal for fragile electronics, glass products, or sensitive food items.
While capable of precise positioning, indexing conveyors subject products to more frequent acceleration and deceleration forces. This start-stop motion can be problematic for unstable or top-heavy items. However, modern indexing systems often incorporate motion control technology to minimize these effects, using sophisticated acceleration/deceleration curves to reduce impact forces by up to 40% compared to basic systems.
Indexing conveyors often provide better control and flexibility in terms of product manipulation at each station for products requiring specific orientation or careful handling during processing. This makes them particularly valuable in assembly operations where components need to be precisely positioned or oriented before the next processing step.
Conclusion
Before deciding between a continuous or indexing rotating conveyor, conduct a detailed time-motion study of your current production process. This analysis will help you quantify your exact speed requirements, identify critical pause points in your operation, and determine precise product handling needs. Armed with this data, you'll be better equipped to make an informed choice that aligns with your specific operational demands and long-term production goals.