


In a world where every millisecond can impact user experience and business outcomes, proactive strategies for managing application performance are more essential than ever. High-performing applications not only foster user loyalty but also drive competitive advantage across industries. This competitive edge is significant as digital consumer expectations rise and businesses compete on the quality and speed of their digital offerings. By adopting a holistic and anticipatory approach, IT teams can safeguard application reliability, scalability, and efficiency—not only preventing disruptions but ensuring consistent improvement over time. Robust application performance monitoring solutions empower organizations to diagnose and resolve issues before users are affected. These solutions also support the ability to anticipate trends, make informed resource allocation decisions, and deliver seamless, high-quality digital experiences across devices and locations.
Organizations that prioritize proactive monitoring and management enjoy fewer outages, faster incident resolution, and improved customer satisfaction. These approaches focus not just on reacting to issues, but on systematically preventing them—a necessity as applications grow more complex and users expect seamless experiences across platforms and devices. Tools like https://www.eginnovations.com/product/application-performance-monitoring help businesses maintain visibility into performance metrics and detect anomalies before they escalate. By establishing a proactive culture that values continuous learning and process improvement, companies position themselves for sustainable growth and resilience. The right strategies enable both technical excellence and business resilience in today’s fast-evolving digital environment, where agility and reliability are indispensable.
Effective application performance begins with real-time, full-stack monitoring. Modern monitoring tools track key metrics, such as response times, error rates, throughput, and server health, to provide actionable insights. These tools allow organizations to observe both the user-facing and back-end layers of the application, identifying performance bottlenecks at any point in the stack. Platforms such as Prometheus and Grafana facilitate visualization of performance trends and historical data, enabling IT teams to detect subtle deviations before they escalate. Granular, end-to-end visibility ensures no aspect of application performance is overlooked—from networking and server issues to database latency and front-end rendering times.
Advanced alerting systems should be calibrated to strike a balance between sensitivity and relevance—alert fatigue can undermine their value, while missing a true anomaly can be costly. This is why the best systems not only send alarms but also contextualize those alerts to drive informed action. Intelligent alerting frameworks use baselines, anomaly detection, and contextual notifications to prioritize alerts based on severity and potential impact. The right combination of thresholds and adaptive learning helps filter out noise, allowing critical events to be recognized quickly and minimizing false positives. This ensures that stakeholders can respond efficiently to incidents and maintain optimal application health without being overwhelmed by irrelevant signals.
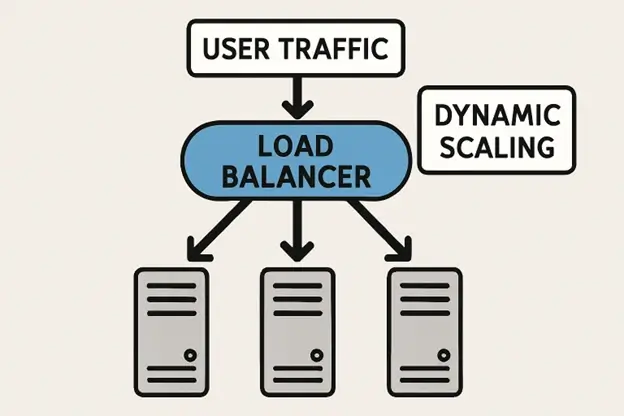
As demand fluctuates throughout the day or in response to marketing events, applications must adapt dynamically. Load balancing technologies distribute incoming requests across multiple servers and data centers, enhancing both availability and performance. By intelligently routing user traffic, load balancers prevent individual servers from becoming overwhelmed, thus avoiding slowdowns and outages that could degrade user trust. For globally distributed audiences, Global Server Load Balancing (GSLB) reduces latency by directing users to the nearest data center, optimizing response times, and improving the overall user experience regardless of geographic location.
Complementing load balancing, auto-scaling mechanisms play a crucial role. These technologies automatically allocate resources during periods of increased traffic, then scale them down to control costs during quieter periods. With auto-scaling, businesses can efficiently align infrastructure capacity with real-time demand, maintaining performance without wasteful over-provisioning. By integrating load balancing and auto-scaling, organizations can achieve high performance and reliability, regardless of user volume.
The efficiency of its underlying code often determines application performance. Even the most potent hardware or advanced infrastructure cannot compensate for poorly designed code. Regular reviews and code profiling with tools like AppDynamics, New Relic, or open-source profilers help identify execution bottlenecks that could cause slow user response times or system crashes. By using profiling, development teams can pinpoint inefficient functions, memory leaks, and excessive resource consumption. Optimizing or refactoring inefficient routines reduces CPU and memory consumption, minimizes technical debt, and delivers improved end-user responsiveness. This proactive attention to code health helps maintain both application speed and maintainability as the codebase evolves.
Beyond basic cleanup, adopting more efficient algorithms and data structures can lead to dramatic gains. For example, replacing nested loops with hash-based lookups or optimizing database queries can have a transformative effect, especially at scale. Integrating performance testing into CI/CD workflows ensures new code meets performance benchmarks early in the lifecycle, rather than after deployment, which can prevent major headaches in production. Comprehensive benchmarking and load testing reveal how changes affect latency and throughput under different workloads.
Certain operations—such as file processing, third-party API calls, or data analytics—can block interactions and degrade responsiveness if performed synchronously. In high-traffic applications, these bottlenecks are particularly problematic, as they can cause slowdowns that ripple through the application. Asynchronous processing frameworks help offload these tasks, freeing the main application thread to handle user requests without delay. By delegating time-consuming or high-latency operations to background jobs or non-blocking handlers, applications can remain highly responsive—even under peak usage conditions.
Fostering collaboration between development and operations is fundamental to proactive performance management. DevOps practices integrate automation, continuous integration (CI), and continuous delivery (CD), enabling rigorous testing and rapid, reliable deployments. Automated pipelines enable the execution of extensive testing, security scans, and performance analysis on every build, allowing for the detection of defects and inefficiencies before they reach production environments. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) enables consistent environment configurations, reducing inconsistencies that often lead to performance issues, and facilitates the easy reproduction and scaling of environments as needed for reliability and incident recovery.
Regular patching and security updates keep applications resilient against emerging threats, ensuring that vulnerabilities are remediated before they can be exploited. Incorporating performance testing in pipeline stages means regressions are caught and addressed early, minimizing production risk and maximizing speed to market. By establishing a feedback loop between monitoring, development, and operations, organizations can continuously iterate and enhance both performance and security. This alignment of teams, tools, and processes fosters an agile, responsive organization that is well-equipped to handle future challenges.
Artificial Intelligence shifts application management from reactive to predictive and autonomous. AI tools analyze real-time data, uncovering patterns and risks before issues occur. These insights help IT teams anticipate spikes, prevent bottlenecks, and identify causes faster than manual methods. Predictive analytics forecast traffic, capacity, and failure points, enabling preemptive action to keep applications running smoothly. Intelligent automation manages routine tasks like infrastructure scaling, patching, and rerouting—reducing operational costs and errors. By automating routine maintenance, engineers can focus on innovation and troubleshooting. AI's evolving capabilities in self-healing and anomaly detection will further enhance proactive performance management. Investing in AI-driven management improves efficiency and ensures high-quality digital experiences.
Proactively managing application performance means combining robust monitoring, dynamic scaling, rigorous code optimization, asynchronous patterns, DevOps collaboration, and smart AI tools. These strategies enable organizations to identify and resolve issues before they impact users, ensuring consistent, high-quality digital experiences. In an era where reliability, speed, and adaptability define success, proactive management techniques are essential for meeting the ever-evolving demands of users and safeguarding business objectives. As application ecosystems become increasingly complex, investing in proactive management is crucial for achieving operational excellence and long-term success.