

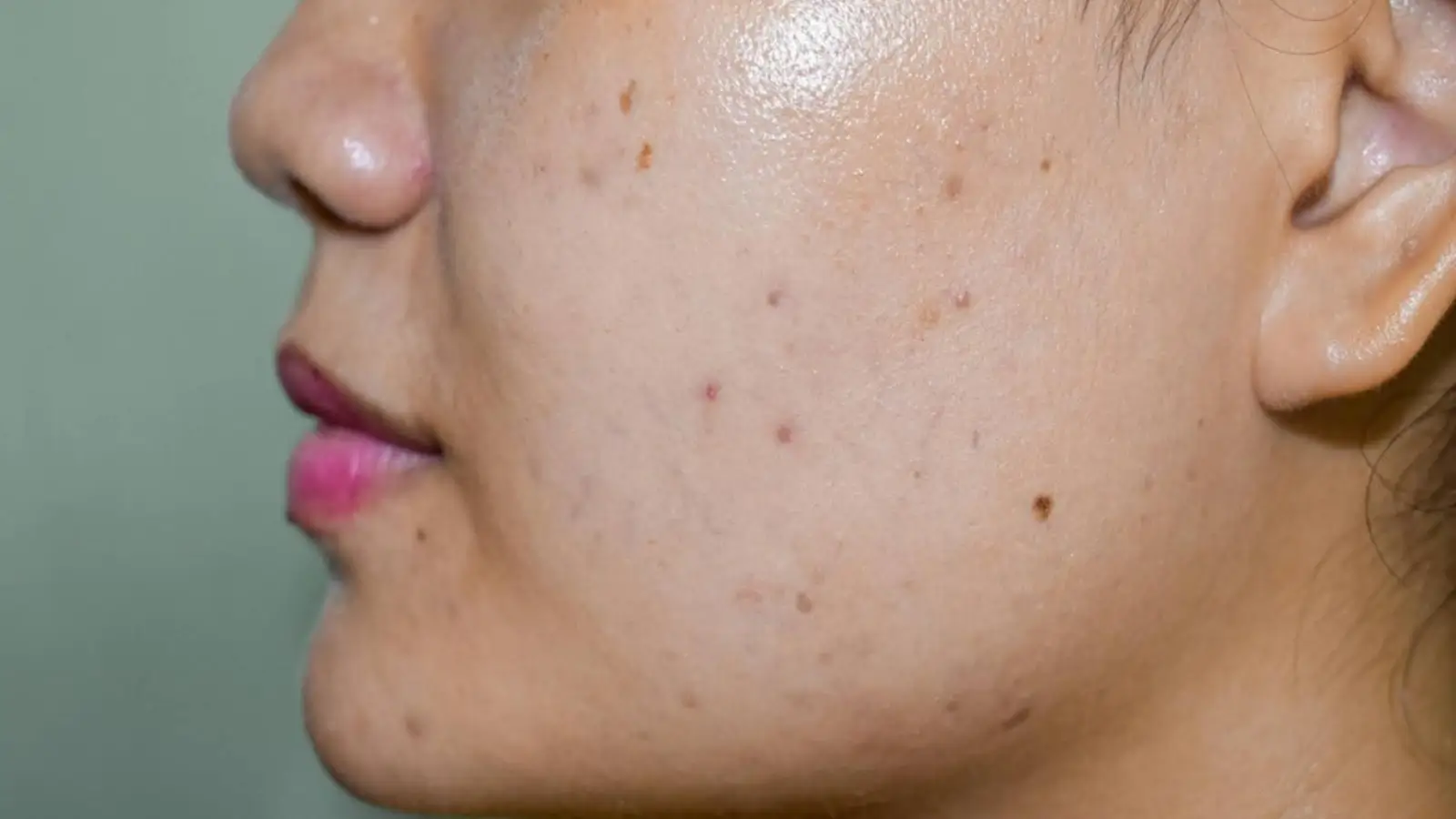
Dark spots, also known as hyperpigmentation, are among the most common skin concerns worldwide. In Australia, where sun exposure is high year-round, these patches of darker pigmentation are especially prevalent. They can appear as acne scars, melasma, age spots, or sun damage, and often make the complexion look uneven.
The good news? There are safe, effective ways to reduce their appearance. This guide breaks down the best dark spot treatment options recommended by dermatologists, the science behind them, and the realistic results you can expect.
Skin colour is determined by melanin, a natural pigment produced by specialised cells called melanocytes. Dark spots form when the skin produces excess melanin in certain areas. In Australia, where UV levels are consistently strong, sun damage is the leading cause of pigmentation. Other common triggers include:
Understanding the underlying cause of your pigmentation is crucial. Tailoring a treatment plan to the root trigger ensures better outcomes and reduces the chance of recurrence.
Dermatologists typically recommend starting with topical solutions, as they are accessible and effective with consistent use. Common options include:
Topical treatments require patience. They often take several weeks of daily use to show visible results. Importantly, sunscreen must always be paired with these products. Without UV protection, dark spots can return or worsen, even while treating them.
For deeper or more resistant pigmentation, professional treatments may be recommended. These include:
While these treatments often deliver faster results, they usually require multiple sessions and some downtime. A consultation with a dermatologist ensures the right procedure is chosen for your skin type and pigmentation pattern.
Lifestyle habits play an essential role in both prevention and long-term success:
Together, these steps help protect against new dark spots forming and improve the effectiveness of topical and in-clinic treatments.
Patience is key with pigmentation. Topical treatments may take 8–12 weeks before noticeable improvement is seen. In-clinic treatments often accelerate results, but typically require multiple sessions spaced weeks apart. Results also depend on factors such as skin type, depth of pigmentation, and sun exposure.
A dermatologist can provide a tailored timeline based on your unique skin needs, helping you set realistic expectations.
While dark spot treatments are generally safe, there are important considerations:
Managing these risks with professional guidance helps balance effectiveness with long-term skin health.
While treating dark spots is achievable, prevention is even more effective. Daily sun protection, healthy skincare habits, and avoiding unnecessary trauma to the skin all reduce the likelihood of developing new pigmentation. By being consistent with these measures, you can maintain results for years to come.
Dark spots are a common but treatable concern. With the right combination of sun protection, consistent topical care, and dermatologist-led procedures when needed, you can achieve a more even and radiant complexion.
For Australians, prioritising daily sun safety is the most effective long-term prevention. If you’re unsure which dark spot treatment is best suited for your skin, consult a qualified dermatologist who can guide you through safe, evidence-based options tailored to your needs, ensuring lasting results and healthier, brighter skin overall.