Streamlining Workloads with Hybrid Cloud Architecture
— Hybrid cloud architecture delivers the flexibility, cost savings, and performance businesses need to excel in an unpredictable digital world.
Key Takeaways
- Hybrid cloud architecture blends private and public cloud resources for maximum flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency.
- Proper planning, ongoing optimization, and integrated management tools are critical for successful hybrid cloud deployment.
- Adopting hybrid cloud strategies supports sustainability efforts and future-proofs IT investments in a rapidly changing digital landscape.
Introduction
As digital transformation accelerates, organizations face mounting pressure to increase agility, manage costs, and enhance productivity. Hybrid cloud architecture has rapidly emerged as a leading solution, empowering businesses to harness the best features of private and public clouds for seamless workload management. By adopting this approach, companies can simplify workloads with a hybrid cloud architecture and improve operational efficiency.
The hybrid model is not just a technology trend—it is a foundational strategy for organizations seeking to remain competitive and future-proof in evolving markets. Integrating on-premises resources with cloud platforms allows companies to optimize costs, ensure business continuity, and meet regulatory requirements without sacrificing innovation.
Organizations that implement hybrid cloud architectures gain significant advantages. The ability to move workloads seamlessly between environments ensures that peak loads, evolving business priorities, and geographic distribution do not become IT bottlenecks. As adoption grows, the hybrid model is redefining how modern businesses architect, scale, and secure their digital operations.
Hybrid cloud’s flexibility and adaptability allow enterprises to support both legacy applications and new, cloud-native development, ensuring that technological advancements do not obsolete existing investments.
Understanding Hybrid Cloud Architecture
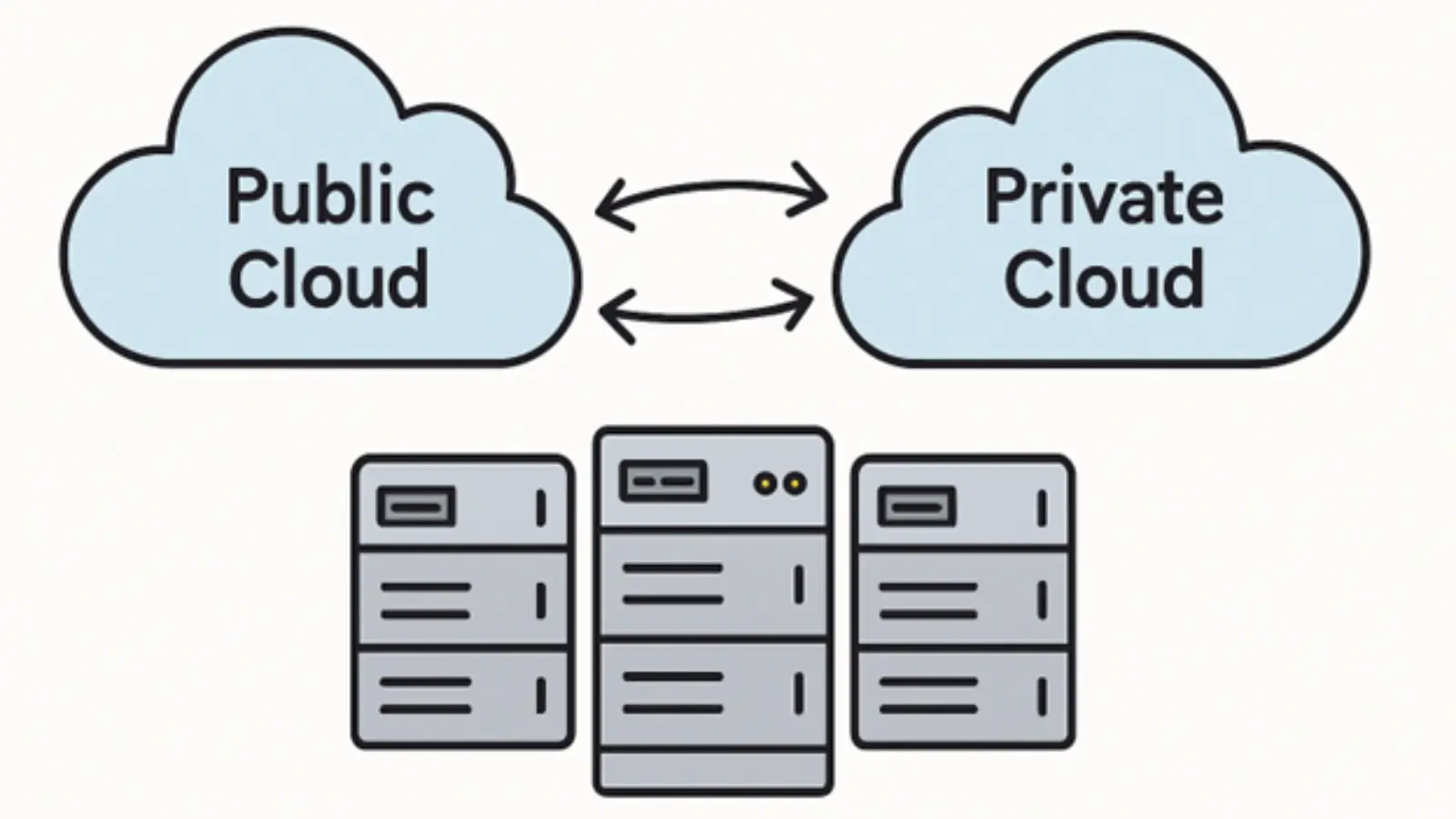
Hybrid cloud architecture combines on-premises private cloud infrastructure with third-party public cloud services. This integration creates a unified, orchestrated environment where data and applications can flow in accordance with business rules, policies, and real-time requirements. The hallmark of hybrid cloud is its agility. Workloads can be deployed, moved, and scaled across environments as business conditions change.
Effective hybrid cloud solutions require robust interconnectivity and secure data transfer mechanisms. Technologies such as containers, APIs, and dedicated network links facilitate interoperability between on-premises and cloud resources. According to CIO, re-architecting IT for multicloud environments involves key steps such as assessing workloads, redesigning infrastructure, and implementing automation to ensure smooth operation across different cloud platforms. The result is a dynamic architecture capable of addressing fluctuating demands, regulatory constraints, and performance requirements, all while reducing the risk of vendor lock-in.
Benefits of Hybrid Cloud for Workload Management
Optimized Resource Allocation
Hybrid cloud platforms enable strategic placement of workloads, matching application requirements to the most suitable infrastructure. Mission-critical or sensitive data can remain within a controlled private environment, while less-sensitive or variable-performance tasks can leverage public cloud scalability and cost structures.
Enhanced Scalability
The dynamic nature of hybrid clouds means organizations can rapidly scale resources during peak demand or launch new applications without upfront hardware investments. Elastic scaling prevents both resource shortages and wasteful over-provisioning.
Cost Efficiency
Leveraging the public cloud for non-sensitive operations helps reduce capital expenditures and operational costs. Private cloud resources handle high-priority workloads with stringent compliance or security demands, ensuring an optimal balance between expenditure and risk management.
Implementing Hybrid Cloud Strategies
Assess Workload Requirements
Start by auditing existing applications and workloads. Evaluate performance expectations, latency, regulatory compliance, and data residency issues to determine which workloads are appropriate for public or private clouds. Understanding these details is vital for effective migration and ongoing optimization.
Ensure Seamless Integration
Choose platforms and tools that support easy interoperability between cloud and on-premises environments. Automation, container orchestration, and hybrid cloud management platforms minimize friction, enabling real-time orchestration of complex workloads.
Monitor and Optimize
Continuous monitoring and analytics are key to controlling costs and aligning workloads with business objectives. Automated tools can help forecast demand, optimize resource allocation, and identify inefficiencies or security vulnerabilities, enabling proactive improvements.
Real-World Applications
Enterprises across industries are leveraging hybrid cloud not only to streamline traditional workloads, but also to support new initiatives in artificial intelligence, big data, and Internet of Things (IoT). For example, some financial and healthcare providers use hybrid clouds to process sensitive data in private environments while leveraging public cloud resources for data analytics and backup.
Studies show that hybrid multicloud infrastructures can reduce data center energy consumption and carbon footprints, a critical consideration as organizations seek to align with sustainability goals. This operational and environmental benefit is helping hybrid cloud become a cornerstone of responsible enterprise IT strategy.
Challenges and Considerations
Complexity in Management
Managing hybrid environments introduces complexity. Disparate systems must be synchronized, monitored, and secured as a cohesive unit. Reliable hybrid cloud management software, strong DevOps culture, and training are crucial to maintain visibility and control.
Security and Compliance
Securing data across hybrid environments is more complex than in single-cloud or on-premises environments. Comprehensive policies for identity, access management, data encryption, and routine audits must be implemented to mitigate risks.
Future Trends in Hybrid Cloud
The evolution of hybrid cloud is accelerating, shaped by advances in artificial intelligence, automation, and cross-cloud orchestration. AI-driven management frameworks are emerging to dynamically allocate resources, automatically respond to workloads, and minimize human intervention. This not only reduces costs but also boosts overall system reliability and security.
As organizations further integrate multi-cloud and edge computing with hybrid solutions, real-time data processing, IoT, and decentralized applications are expected to proliferate.
Conclusion
Hybrid cloud architecture delivers the flexibility, cost savings, and performance businesses need to excel in an unpredictable digital world. When thoughtfully implemented, hybrid strategies enable organizations to make the most of both private and public resources—empowering them to scale, innovate, and compete more effectively today and into the future.