Cloud Services: Transforming Modern Business Infrastructure for Scalability, Security, and Efficiency
— Cloud Services have become essential for organizations looking to optimize operations, enhance security, and innovate without limitations.

Cloud Services have rapidly become the backbone of modern digital transformation, enabling businesses of all sizes to scale smarter, operate faster, and innovate with fewer limitations. Today’s organizations are no longer debating whether to adopt cloud technology—they’re designing strategies on how to use it more efficiently across hybrid, multi-cloud, and edge environments. With increased demands for remote collaboration, real-time analytics, enhanced storage, and cost-effective IT operations, Cloud Services are the key to staying resilient and competitive in a fast-evolving landscape.
Understanding Why Cloud Services Matter Today
At the core, Cloud Services allow businesses to store data, deploy applications, run workloads, and streamline operations without relying on traditional, hardware-heavy infrastructures. Instead of maintaining expensive servers or over-expanded IT teams, organizations leverage cloud platforms to reduce cost, improve performance, and access resources instantly.
Whether a startup needs flexible hosting, or an enterprise is looking for intelligent automation and global accessibility, the cloud ensures these capabilities are accessible, fast, and secure.
The Big Shift: From Traditional IT to Cloud-First Strategies
The business world is shifting aggressively toward cloud-first strategies—where the cloud is not just an enhancement, but the primary foundation of IT operations. Companies that once relied entirely on physical data centers are now recognizing the limitations of legacy systems:
-
Slow deployment times
-
High maintenance costs
-
Limited scalability during peak demand
-
Increased risks during outages or disasters
Cloud Services solve these issues by offering elasticity, uptime guarantees, automated backups, and decentralized access. This shift has made workplace efficiency and business continuity significantly stronger than before.
Types of Cloud Services Shaping Modern Enterprises
While the cloud ecosystem is vast, most solutions fall into three functional categories. Understanding these helps businesses choose the right approach:
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides virtual servers, networks, and storage on demand. It’s ideal for companies wanting full control over operating systems and applications without managing hardware.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS simplifies the development process by offering preconfigured environments, databases, and development tools. It’s widely used by software teams that want to focus on coding rather than infrastructure setup.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers ready-to-use applications over the internet—CRM tools, email platforms, office suites, analytics dashboards, and more. This model is cost-effective, secure, and easy to scale across teams.
These three layers work together to create a cloud ecosystem where businesses can customize how much control or automation they need.
How Cloud Services Strengthen Business Operations
The most powerful advantage of cloud adoption is its ability to improve multiple areas of operations simultaneously. Organizations benefit through:
1. Scalability When You Need It
Instead of planning hardware purchases months in advance, Cloud Services scale instantly with user demand. Whether it’s seasonal spikes, application traffic, or growing team sizes, the cloud adjusts resources automatically.
2. Cost Efficiency Without Sacrificing Performance
Cloud platforms operate on a pay-as-you-go model. Companies stop paying for unused resources and only invest in what they actively consume. This eliminates heavy upfront investment and reduces long-term operational expenses.
3. Stronger Security and Compliance
Leading cloud providers implement enterprise-level security—data encryption, identity management, multi-region backups, and automatic threat detection. For organizations handling sensitive data, compliance frameworks are already built in.
4. Improved Collaboration Across Distributed Teams
With remote and hybrid work becoming normal, Cloud Services ensure team members can access applications, files, and communication tools from anywhere with consistent performance.
5. Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Cloud backup and replication features keep data safe even in the event of outages, cyberattacks, or accidental loss. Recovery is faster, smoother, and far more reliable than traditional methods.
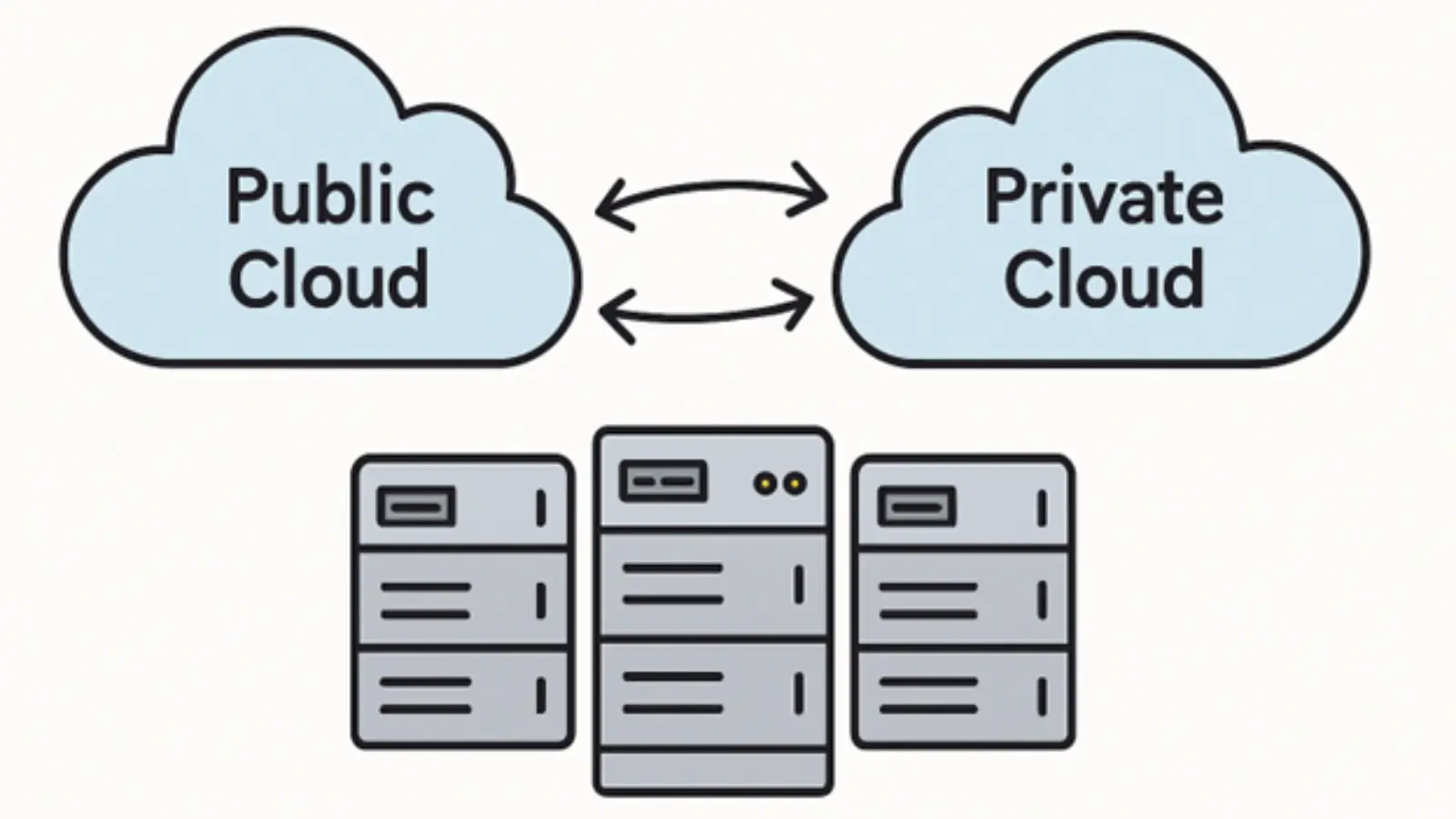
Why Businesses Are Moving Toward Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Models
While public cloud adoption is rising, many organizations are choosing hybrid and multi-cloud environments for better flexibility and control.
Hybrid Cloud
Combines on-premises infrastructure with cloud platforms, offering balance for companies needing both local security and cloud scalability.
Multi-Cloud
Uses multiple cloud providers—AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, Oracle Cloud—to avoid vendor lock-in and optimize cost, performance, and reliability.
Both strategies allow organizations to use the best features of multiple environments while tailoring their infrastructure to specific workloads.
The Role of Cloud Services in Innovation
Cloud technology is not just about storage or servers—it’s the gateway to advanced innovations such as:
-
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
-
Internet of Things (IoT) automation
-
Big Data analytics
-
Real-time monitoring and predictive insights
-
High-performance computing
-
Edge computing
These capabilities empower businesses to build smarter applications, improve customer experiences, and innovate faster than competitors tied to older systems.
Industries That Benefit the Most from Cloud Services
Although nearly every sector is adopting the cloud, some industries are experiencing transformative outcomes:
-
Finance: Secure data processing, fraud detection, digital banking
-
Healthcare: Telemedicine, EHR systems, medical imaging storage
-
Retail: Inventory automation, eCommerce, customer personalization
-
Manufacturing: IoT-connected machinery, supply chain optimization
-
Education: Online learning platforms, virtual classrooms
-
Technology & SaaS companies: Faster development cycles and global scalability
The cloud offers each of these industries the ability to modernize their services while cutting down operational overhead.
Challenges and Misconceptions About Cloud Services
Despite the advantages, some organizations hesitate due to misconceptions. Common concerns include:
“The cloud isn’t secure.”
In reality, cloud security is often stronger than local systems due to routine patching, encryption, and 24/7 monitoring by global experts.
“Migration is too complex.”
Modern migration tools automate much of the work, and most cloud providers offer step-by-step support during the transition.
“Cloud costs might spiral out of control.”
With the right configuration and monitoring, businesses can easily track, predict, and optimize spending.
Addressing these doubts helps companies realize that the cloud is a long-term asset, not a risk.
What the Future of Cloud Services Looks Like
Cloud technology continues to evolve, and the next phase will revolve around:
-
Edge computing for real-time processing
-
AI-driven automation for IT operations
-
Serverless architectures for cost reduction
-
More robust multi-cloud ecosystems
-
Enhanced sustainability in data centers
-
Quantum computing integration
Businesses that embrace these advancements will stay ahead of the competition as technology continues to grow smarter and faster.
Final Thoughts
Cloud Services have become essential for organizations looking to optimize operations, enhance security, and innovate without limitations. Whether a business is preparing for global expansion, improving internal workflows, or modernizing its infrastructure, the cloud offers scalable, flexible, and future-ready solutions.
As industries continue to shift toward digital-first models, investing in Cloud Services isn’t just a technological upgrade—it’s a strategic step toward long-term success and resilience.